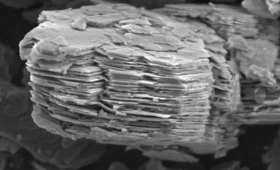
The first observation of a super-hydrated phase of the clay mineral kaolinite could improve the understanding of processes that lead to volcanism and affect earthquakes.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore scientists and colleagues are working on a NASA project to study microorganisms in a Nevada hot spring that could determine whether extraterrestrial life exists.
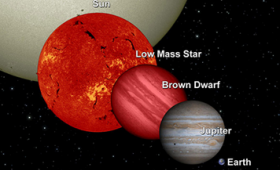
Laboratory scientists have conducted three experiments at the National Ignition Facility to study conditions relevant to matter in brown dwarfs—"failed stars."
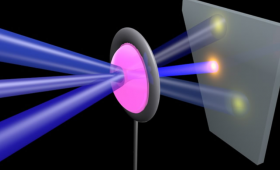
A team of Livermore researchers successfully combined several separate National Ignition Facility lasers into a “superbeam” for the first time.

The American Heart Association (AHA) and Lawrence Livermore have formed a strategic business partnership to overcome the burden of drug discovery, cost, and access.
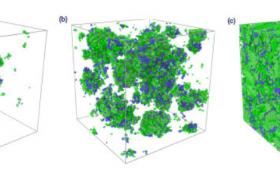
Livermore researchers and their collaborators have achieved a breakthrough in 3D printing one of the most common forms of marine grade stainless steel—a low-carbon type called 316L—that promises an unparalleled combination of high-strength and high-ductility properties.

A new consortium will combine vast data stores, supercomputing, and scientific expertise to reinvent the discovery process for cancer medicines.

Scientists at the Laboratory have worked with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and U.S. Navy laboratories on the Tactical Undersea Network Architectures, or TUNA, initiative.

To help increase the U.S. supply of rare earth metals, a Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory team has created a new way to recover rare earths using bioengineered bacteria.