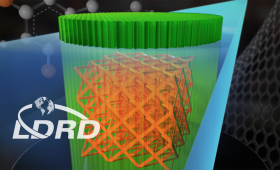
Livermore researchers have discovered novel ways to extend the capabilities of two-photon lithography, a 3D printing technique that produces features smaller than one-hundredth the width of a human hair.
Science and Technology Highlights
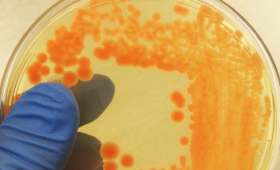
Livermore scientists are studying a new “tunable” biosurfactant that is environmentally friendly and can have broad industrial utility.

A Lawrence Livermore biomedical technology that can deliver vaccines and drugs inside the human body has been licensed for use in cancer treatments.

Livermore scientists and engineers have developed a “brain-on-a-chip” device aimed at testing and predicting the effects of biological and chemical agents, disease, or pharmaceutical drugs on the brain.
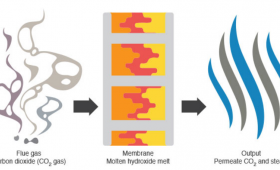
Livermore scientists have developed a new CO2 separation technology using molten hydroxide.

Lawrence Livermore researchers released 62 newly declassified videos of atmospheric nuclear tests films that have never before been seen by the public.

The L3-HAPLS (High-Repetition-Rate Advanced Petawatt Laser System), developed by Livermore, has been installed at the ELI Beamlines Research Center in the Czech Republic.

Thin-film microelectrode arrays produced at the Laboratory have enabled development of an automated system to sort brain activity by individual neurons.

Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and their collaborators have discovered how to build complex 3D parts in a fraction of the time of traditional layer-by-layer printing using a process called volumetric 3D printing.

Arctic sea ice loss of the magnitude expected in the next few decades could impact California’s rainfall and exacerbate future droughts, according to new research led by the Laboratory.