A research team from Livermore, the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Rochester provides the first experimental evidence for superionic conduction in water ice at planetary interior conditions.
Science and Technology Highlights
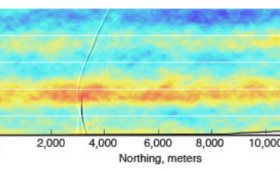
A Livermore team recently completed a project to develop a first-of-its-kind seismoacoustic simulation capability.

Livermore researchers are studying the microbiome of the international space station

The Laboratory’s long history of developing and supporting open source software has led to thriving user communities and international collaborations.

Researchers have discovered that a material that can convert light into electricity, perovskite, can also switch between transparent and non-transparent states, making it useful as an energy-efficient, switchable window.

We ask three scientists to explain what algae is and why it's interesting to scientists and the world. (Video)
Researchers have identified evidence of early chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) brain pathology after head impact, even in the absence of signs of concussion.
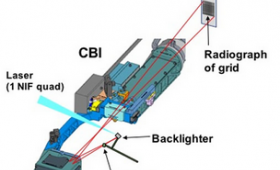
When a fast x-ray camera was successfully coupled to a sophisticated x-ray optic and mounted recently in NIF, it brought powerful new diagnostic capabilities to the world’s highest-energy laser system.

The development and potential applications of laser wakefield acceleration-driven light sources are featured in an article in the January issue of Optics & Photonics News.
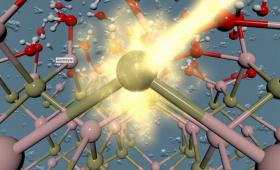
Livermore researchers and colleagues have developed an integrated theory-experiment technique to interrogate chemistry at solid/liquid interfaces, with the goal of developing better methods of generating hydrogen fuel from solar power.

