Science and Technology Highlights
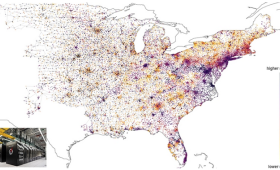
To advance the modeling and computational techniques needed to develop more efficient grid-control strategies under emergency scenarios, a multi-institutional team has used a LLNL-developed software capable of optimizing the grid’s response to potential disruption events under different weather scenarios, on Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Frontier supercomputer.

In early May, the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Megajoule Neutron Imaging Radiography Experiment (MJOLNIR) team’s dense plasma focus (DPF) achieved greater than 1012 neutrons in a single deuterium

A new study provides surprising behavior of hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes.

To learn about the properties of materials under changing temperatures and pressures, researchers typically combine laboratory experiments with theoretical models and computer simulations.

Optics researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have refined their novel metasurface process to create taller features without increasing feature-to-feature spacing, an advance that unlocks exciting new design possib

The detailed HPC design uses the world’s largest supercomputers and its most complicated simulation tools to help subject-matter experts choose new directions to improve experiments. CogSim then employs artificial intelligence (AI) to couple hundreds of thousands of HPC simulations to the set of past ICF experiments.
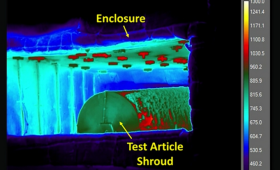
LLNL and Sandia National Laboratories recently successfully executed the second joint abnormal thermal environment (ATE-2) test for the W80-4 Life Extension Program (LEP). ATE-2 was a fast-heat, fully engulfing system-level fuel fire test, the first for LLNL in more than three decades.

Scientists at LLNL performed simulations using the Lab's supercomputer Ruby to uncover physical mechanisms that explain why humidity controls the rate of atmospheric corrosion of aluminum metal.

In a new study in Nature Sustainability, an LLNL scientist and collaborators examined concurrent SOC and yield responses to cover cropping, including their direct connection.

