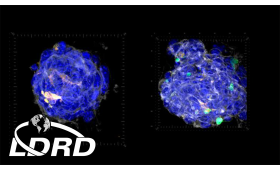
Livermore scientists found that proteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM) can dramatically impact the immune system’s ability to kill tumors.
Science and Technology Highlights
Livermore researchers and their colleagues are exploring ways to build laser optics from plasma.

Livermore’s decades of leadership in developing high-energy lasers is being tapped to provide a key component of a major upgrade to SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Linac Coherent Light Source.
A new study by researchers at Lawrence Livermore and the University of California, San Francisco, identifies cancer-related risks for poor outcomes from COVID-19.
An international team turned to Lawrence Livermore’s National Ignition Facility to help unravel the inner workings of heat conduction in clusters of galaxies—the largest structures in the universe.

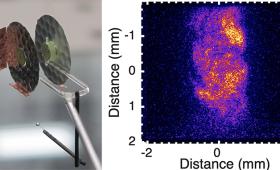
In findings that could help advance another “viable pathway” to fusion energy, research led by Livermore physicists has proven the existence of neutrons produced through thermonuclear reactions from a sheared-flow stabilized Z-pinch device.

A new review by Livermore scientists and collaborators, appearing in Nature Reviews Microbiology, describes how living and dead microorganisms strongly influence terrestrial biogeochemistry by forming and decomposing soil organic matter

An international team of scientists has found new biomarkers that can be used for diagnostic purposes and potentially as predictive tools of the risks associated with deep-space flight.

Livermore scientists have provided input on Microsoft’s pathway to become carbon-negative by 2030.

Livermore scientists used molecular dynamics simulations to describe the dynamical behavior of dissolved metal ions and water, a key to better understanding the process of corrosion.