The Laboratory has developed a new technique that enhances the performance of its flexible thin-film biological sensors,
Science and Technology Highlights

Multi-institutional research team develops a new system to control gene expression in laboratory bacteria.

Combining 3D printing through extrusion-based direct ink writing and an alloying and dealloying process, researchers have engineered nanoporous gold.

A research team announced the discovery of the Higgs boson particle transforming into bottom quarks as it decays.

A team of Livermore scientists has developed an expanded nuclear fission chain theory and detectors.

Researchers are developing new deep learning and high-performance computing algorithms that can sift through massive amounts of data for evidence of nuclear proliferation activities.
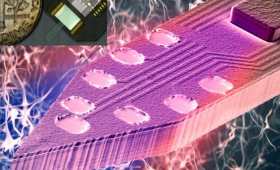
A research team has taken a major step forward in enabling “multicolor” optogenetic control of different neuron types.

An LLNL–Virginia Tech team reported producing micro-architectured 3D graphene aerogel structures with higher resolution and complexity than anything created before with other 3D printing methods.

A research team led by scientists at Lawrence Livermore describes optical measurements of the insulator-to-metal transition in fluid hydrogen.
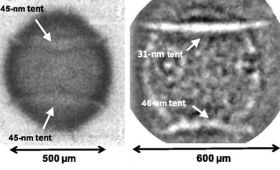
Livermore scientists are working to mitigate the adverse effects on National Ignition Facility implosion performance of the gossamer-thin membranes known as “tents” that support the target capsule in the hohlraum.

