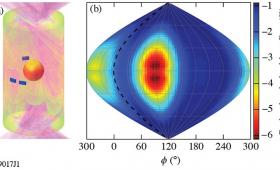
Data correlating two factors that lead to implosion asymmetries have brought LLNL scientists a step closer to understanding the gap between simulations and performance of inertial confinement fusion experiments.
Science and Technology Highlights

Livermore scientists have paired 3D-printed, living human brain vasculature with advanced computational flow simulations to better understand tumor cell attachment to blood vessels.

Researchers find that more than 50 percent of the world’s oceans already could be impacted by climate change.

A research team optimizes catalyst performance by studying the effect of pretreatment-induced nanoscale structural and compositional changes on catalyst activity and long-term stability.

A Livermore team has published new supercomputer simulations of a magnitude 7.0 earthquake on the Hayward Fault, the highest-ever resolution ground motion simulations on this scale.

A research team has combined machine learning, 3D printing, and high-performance computing simulations to accurately model blood flow in the aorta.

Livermore researchers have increased the complexity of neuronal cultures grown on microelectrode arrays.

Researchers at Livermore and an international team of collaborators have developed an experimental capability for measuring the basic properties of matter at the highest pressures thus far achieved in a controlled laboratory experiment.

Massive compressive shearing forces generated by the tidal pull of Jupiter-like planets on their rocky ice-covered moons may form a natural reactor that drives simple amino acids to polymerize into larger compounds.

Livermore researchers are perfecting a technology called reversible electrophoretic deposition for high-contrast wearable displays.