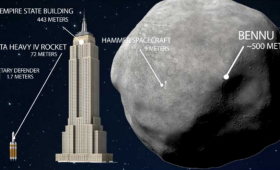
Livermore scientists scientists are part of a national planetary defense team that designed a conceptual spacecraft to deflect Earth-bound asteroids.
Science and Technology
in the News
Science and Technology
in the News
News Center
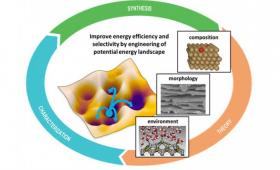
Lawrence Livermore scientists have received funding improve the energy efficiency of copper-based catalysts to convert carbon dioxide into methane and other valuable hydrocarbon products.

This video describes the work of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's National Ignition Facility.

Two researchers affiliated with Lawrence Livermore, a current employee and a retiree, have been named fellows of the international Combustion Institute (link is external) (CI).

Livermore scientists observe the first experimental evidence of a noble gas element reacting with a metal.
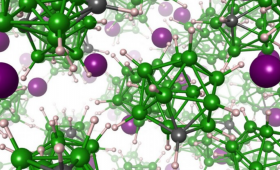
An international collaboration jointly led by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is studying materials for solid-state lithium-ion batteries.

A team of Livermore researchers is developing networks capable of "collaborative autonomy"

The research team characterizes the detailed shock response of several variations in a single base polymer.

Lawrence Livermore researchers are developing lasers that are both high-powered and “eye-safer” to reduce the danger of retinal damage to bystanders from exposure to scattered laser light.

Bigfoot is an experimental platform designed to control implosion symmetry and hydrodynamic instabilities, improve predictability, and enhance the delivery of laser energy to NIF’s targets.